July 24, 2021 Speech Recognition
Fairseq의 Wav2vec 2.0 Pretrain 실행방법
Fairseq의 제공하는 Wav2vec 2.0 모델의 작동과정을 소개하고자 합니다.
- 본 게시글은 아래의 github를 참고하였습니다.
- https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq.git
- https://github.com/mailong25/self-supervised-speech-recognition.git
Pretraining using self-supervised learning
hydra_train.py를 이용해 pretrain이 진행할 수 있습니다.- 데이터, 모델 파라미터를 설정하기 위해 config 정보가 필요한데요.
--config-dir: config 정보가 담겨져 있는 폴더--config-name: config에 대한 정보가 key, value로 저장되어 있는 yaml 파일이름
wav2vec2_base_librispeech.yaml파일에 입력된 정보
common:
fp16: true
log_format: json
log_interval: 100
checkpoint:
save_interval_updates: 10000
keep_interval_updates: 1
no_epoch_checkpoints: true
task:
_name: audio_pretraining
data: /home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/temp
max_sample_size: 250000
min_sample_size: 32000
normalize: false
dataset:
num_workers: 6
max_tokens: 1200000
skip_invalid_size_inputs_valid_test: true
distributed_training:
distributed_world_size: 2
ddp_backend num_workers: 6
max_tokens: 1200000
skip_invalid_size_inputs_valid_test: true
distributed_training:
distributed_world_size: 2
ddp_backend: no_c10d
criterion:
_name: wav2vec
infonce: true
log_keys: ["prob_perplexity","code_perplexity","temp"]
loss_weights: [0.1, 10]
optimization:
max_update: 800000
lr: [0.0005]
optimizer:
_name: adam
adam_betas: (0.9,0.98)
adam_eps: 1e-06
weight_decay: 0.01
lr_scheduler:
_name: polynomial_decay
warmup_updates: 10000
model:
_name: wav2vec2
quantize_targets: true
final_dim: 256
encoder_layerdrop: 0.05
dropout_input: 0.1
dropout_features: 0.1
feature_grad_mult: 0.1
encoder_embed_dim: 768
python fairseq/fairseq_cli/hydra_train.py \
--config-dir config/pretraining \
--config-name wav2vec2_base_librispeech
- 앞서 입력으로 준
wav2vec2_base_librispeech.yaml파일의 이름이cfg_name에 저장됨cfg_name=”wav2vec2_base_librispeech”
hydra_init을 수행하여 argparser의 default가 업데이트 됨
hydra_init(cfg_name) # 파라미터 설정
hydra_main() # train 수행
hydra_main()이 시작되면, decorator 함수인@hydra.main에 의해cfg의 변수선언이 됨cfg의 값을 보면 아래의 값이 업데이트가 된 것을 확인할 수 있음
'task': {'_name': 'audio_pretraining',
'data': '/home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/temp'
- GPU를 사용할 경우
hydra_main()는 실질적으로 앞서 생성한 cfg와 pre_main을 함수를 불러와 multi-gpu 학습이 이루어짐
distributed_utils.call_main(cfg, pre_main)
먼저
distributed_utils.call_main의 역할인 gpu 분산처리 작동 과정에 대해서 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
distributed call main 이해하기
cfg.distributed_world_size는 gpu 개수 만큼 설정할 수 있음- gpu가 2개면
2로 설정
- gpu가 2개면
rank는 gpu 순서를 의미- 분산처리를 위한
port는 10000, 20000 사이의 랜덤 샘플(e.g. 14630)이 이루어짐- tcp://localhost:14630 (distributed_init_method으로 명칭)
- 다음으로,
torch.multiprocessing.spawn이라는 api를 이용해 분산처리가 진행됨distributed_main: gpu 분산처리 관련 함수args=(main, cfg, kwargs)는 수행하고자 하는 함수(모델함수) 관련된 입력npros의 경우에는 gpu 개수나 world size의 최소개수로 정의됨torch.multiprocessing.spawn( fn=distributed_main, args=(main, cfg, kwargs), nprocs=min( torch.cuda.device_count(), cfg.distributed_training.distributed_world_size, )
distributed_main
main함수(model training)를 수행하기전에 gpu 개수만큼의 localhost을 생성i는 해당 gpu rank를 의미
distributed_main(i, main, cfg: FairseqConfig, kwargs)
- 개별 gpu마다 method 실행
-
첫번째 gpu에 대한 예시 (rank=0)
2021-07-21 12:03:21 | INFO | fairseq.distributed_utils | distributed init (rank 0): tcp://localhost:19502- 먼저, 수행할 gpu를 선정
cfg.distributed_training.device_id = 0 torch.cuda.set_device(cfg.distributed_training.device_id) -
init_process_group: 게별 gpu 마다
hostserver를 여는 과정dist.init_process_group( backend='nccl', init_method='tcp://localhost:19502', world_size=2, # gpu 2개 rank=0 # 0th gpu )
- 먼저, 수행할 gpu를 선정
-
두번째 gpu(rank=1)도 동일한 과정을 거침
- 이 작업이 완료되면 실제 학습시키려고 하는
main()함수가 실행이 됨
여기서 부터 실질적인 Wav2vec 2.0 구조를 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
load_dataset
- 먼저, 사전에 입력데이터 경로 파일 생성을 해야함
python3 examples/wav2vec/wav2vec_manifest.py examples/unlabel_audio --dest /home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/temp --ext wav --valid-percent 0.05 - 세부적인 옵션은 아래와 같습니다.
- fairseq 폴더에서 아래와 같이 명령어 수행해 주면
temp폴더에train.tsv,valid.tsv를 제공 examples/unlabel_audio는 audio file이 있는 경로examples/unlabel_audio/ ├── LJ001-0013.wav ├── LJ001-0025.wav ├── LJ001-0030.wav ├── LJ001-0041.wav ├── LJ001-0042.wav ├── LJ001-0048.wav ├── LJ001-0051.wav ├── LJ001-0064.wav ├── LJ001-0086.wav ├── LJ001-0092.wav ├── LJ001-0097.wav └── LJ001-0100.wav/home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/temp는 생성 결과물(train.tsv,valid.tsv)을 저장하는 경로temp ├── train.tsv └── valid.tsvtrain.tsv의 파일을 아래와 같이 작성되어 있음- folder path
- filename.${ext}, n_frames
/home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/examples/unlabel_audio LJ001-0051.wav 77762 LJ001-0013.wav 41353 - fairseq 폴더에서 아래와 같이 명령어 수행해 주면
- 이렇게 생성된 manifest(
train.tsv,valid.tsv)는main()의 입력으로 들어갑니다. - 여기서부터, 오디오파일을 불러오는 코드와 연결되고 변수들이 아래와 같이 할당되어 있다고 가정
manifest = '/home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/temp/valid.tsv' task_cfg.sample_rate = 16000 self.cfg.max_sample_size = 250000 # related to batch size self.cfg.min_sample_size = 32000 min_sample_size은 사전에 계산해논 manifest의 n_frames과 비교해서 2초(32000/16000(sec))보다 작으면 해당 데이터를 제외하는 방식이 채택됨max_sample_size: frame 개수가max_sample_size도달할때가지 batch set을 만들게 됨FileAudioDataset( manifest, sample_rate=task_cfg.sample_rate, max_sample_size=self.cfg.max_sample_size, min_sample_size=self.cfg.max_sample_size, min_length=self.cfg.min_sample_size, pad=False, normalize=False )
build_model
-
model_cfg를 입력으로 받음{'_name': 'wav2vec2', 'quantize_targets': True, 'final_dim': 256, 'encoder_layerdrop': 0.05, 'dropout_input': 0.1, 'dropout_features': 0.1, 'feature_grad_mult': 0.1, 'encoder_embed_dim': 768} - ARCH_MODEL_REGISTRY에는 다양한 모델 key가 존재하며, mapping 함수를 통해 해당 모델을 불러옴
dc는 특정모델의 config로 기존cfg와 통합되어 합쳐짐model = ARCH_MODEL_REGISTRY['wav2vec2'] # model structure dc = MODEL_DATACLASS_REGISTRY['wav2vec2'] # model configs
Forward
data/audio/raw_audio_dataset.py의 파일이 사용이 되며, trainer가 수행될 때 batch data는 아래의 방식으로 생성됨- example
- fname=
/home/donghwa/Documents/PR/self-supervised-speech-recognition/examples/unlabel_audio/LJ001-0025.wav - wav.shape: (141849,)
def __getitem__(self, index): import soundfile as sf fname = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.fnames[index]) wav, curr_sample_rate = sf.read(fname) feats = torch.from_numpy(wav).float() feats = self.postprocess(feats, curr_sample_rate) return {"id": index, "source": feats}
- fname=
- example
- 결과 예시
{'id': 9, 'source': tensor([-1.5259e-04,...0000e+00])} - 해당 데이터 셋에 대해서 학습하기 위한
permutation과 대응되는 frame_size를 정렬해줌order [array([2, 9, 6, 4, 0... 7, 8, 5]), [106740, 141849, 94109, 131818, 101168, 137391, 110641, 127731, 79248, ...]] - frame이 긴 순서대로 정렬합니다.
np.lexsort(order)[::-1] array([1, 5, 3, 7, 6, 9, 0, 4, 2, 8]) - 해당
getitem으로 얻어진 샘플들은 colleate_fn으로 추가 전처리가 됨 - 총 8개의 데이터에 대해서 각 오디오의 frame의 개수는 아래와 같음
sizes = [len(s) for s in sources] [141849, 137391, 131818, 127731, 110641, 108412, 106740, 101168] - 앞서 구한 indice와, max_tokens(max_length), required_batch_size_multiple(batch_size)를 이용해 batch dataset을 구성한 indice 생성
- required_batch_size_multiple (int, optional): require batch size to be less than N or a multiple of N (default: 1).
cfg.dataset.required_batch_size_multiple= 8cpyhon의 형태를 가진data_utils_fast.pxy로 batch sampler 생성
batch_sampler = dataset.batch_by_size(
array([1, 5, 3, 7, 6, 9, 0, 4, 2, 8]),
max_tokens=1200000,
max_sentences=None, # default
required_batch_size_multiple=8, # default
)
batch_sampler
[array([1, 5, 3, 7, 6... 9, 0, 4]), array([2, 8])]
self.max_sample_size=250000보다 작거나 가장 작은 샘플size를 기준을 최대 target길이로 정함 (pad 없이하는 것이 default)
target_size = min(min(sizes), self.max_sample_size)
- 가장 길이가 짧은 것을 기준으로 wav가 cropping 되게 같은 길이로 맞춰줌
collated_sources.shape
torch.Size([8, 101168])
- 위 과정을 통해
train.py의line 238의sample은 batch 데이터를 생성
samples[0]['net_input']['source']
tensor([[-1.2207e-04, -3.0518e-04, -2.4414e-04, ..., -3.1464e-02,
-2.1545e-02, -3.8574e-02],
[ 3.0518e-04, 3.0518e-05, 1.8311e-03, ..., 2.8076e-03,
3.5095e-03, 4.7913e-03],
[ 2.0752e-03, -5.4626e-03, 6.1340e-03, ..., -1.4038e-03,
-1.2512e-03, -1.4954e-03],
...,
[ 4.1199e-03, 1.7395e-03, -6.1035e-05, ..., -5.4016e-03,
9.4299e-03, 4.4250e-03],
[ 1.7792e-02, 2.5330e-02, 2.6520e-02, ..., -6.1646e-03,
-5.0659e-03, -4.1504e-03],
[ 1.4648e-03, -4.5776e-04, -1.3428e-03, ..., -1.5259e-04,
-1.5259e-04, 0.0000e+00]])
samples[0]['net_input']['source'].shape
torch.Size([8, 101168])
1.convolution
- 먼저 stride를 (
10/2/2/2/2/2)의 값으로 오디오 sequence를 320배 압축 - 아래의 예시는 kernel 512개를 사용한 예제
- feature에 대한 gradient를 0.1로 scale하는 단계가 들어가는데 업데이트 조금씩 주기 위함인 것으로 판단
features = self.feature_extractor(source)
def forward(self, x):
''''
input: x.shape
torch.Size([8, 101168])
# output : x.shape
torch.Size([8, 512, 315])
'''
# BxT -> BxCxT
x = x.unsqueeze(1)
for conv in self.conv_layers:
x = conv(x)
return x
if self.feature_grad_mult > 0:
features = self.feature_extractor(source)
if self.feature_grad_mult != 1.0:
'''
gradiant scaling
'''
features = GradMultiply.apply(features, self.feature_grad_mult)
2.normalization
- feature dimension 축을 가장 뒤로 보낸뒤, 해당 축에 대한 normalization이 진행
- 그리고, unmasked_features용으로 feature를 복사
# torch.Size([8, 512, 315]) => torch.Size([8, 315, 512])
features = features.transpose(1, 2)
features = self.layer_norm(features)
unmasked_features = features.clone()
3.projection & dropout
- feature를 더 높은 차원으로 임베딩
0.1의 비율만큼 dropout이input feature,unmasked feature에 적용됩니다.
if self.post_extract_proj is not None:
'''
features.shape
torch.Size([8, 315, 512]) => torch.Size([8, 315, 768])
'''
features = self.post_extract_proj(features)
features = self.dropout_input(features)
unmasked_features = self.dropout_features(unmasked_features)
features.shape
torch.Size([8, 315, 768])
unmasked_features.shape
torch.Size([8, 315, 512])
4.quantization
- 산출지표
num_vars: number of quantized vectors per group (320)code_ppl: entropy for one-hot vecotor for masked ground trouthprob_ppl: entropy for softmax for masked ground trouthcurr_temp: temperature scale
- Mask 부여
cfg.mask_length는10으로 default로 설정되어 있음self.mask_prob는0.65만큼의 mask가 부여self.mask_selection
def apply_mask(self, features, padding_mask):
if self.mask_prob > 0:
mask_indices = compute_mask_indices(
shape = (8, 315),
padding_mask = None,
mask_prob = 0.65,
mask_length = 10,
mask_type = 'static', # fixed size
mask_other = 0.0,
min_masks=2, # minimum number of masked spans
no_overlap=False, #if false, will switch to an alternative recursive algorithm that prevents spans from overlapping
min_space=1, # only used if no_overlap is True, this is how many elements to keep unmasked between spans
)
mask_indices = torch.from_numpy(mask_indices).to(x.device)
x[mask_indices] = self.mask_emb
min_masks=2보다 커야된다고 설정했지만,데이터 길이의 65%(204.75)는mask_length=10짜리20개로 설정할수 있으며, 더 크므로 20개의 num_mask가 수행됨
'''
compute_mask_indices function 핵심 코드 부분
'''
all_num_mask = int(
# add a random number for probabilistic rounding
mask_prob * all_sz / float(mask_length)
+ np.random.rand()
)
all_num_mask = max(min_masks, all_num_mask)
mask_length길이 단위로데이터 길이의 65%(204.75)를 다룰려면mask_length=10짜리20개가 있어야 함
if mask_type == "static":
lengths = np.full(num_mask, mask_length)
'''
lengths
array([10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10,
10, 10, 10])
'''
- frame_length 범위(315)에서 mask의 시작점을 뽑기위해 한개의 mask 길이을 빼고(305) 무작위로 mask 개수만큼 뽑음
mask_idc = np.random.choice(sz - min_len, num_mask, replace=False)
mask_idc
array([ 80, 298, 72, 253, 218, 89, 37, 228, 163, 287, 224, 240, 58,
59, 185, 268, 164, 289, 304, 112])
mask_idc = np.asarray(
[
mask_idc[j] + offset
for j in range(len(mask_idc))
for offset in range(lengths[j])
]
)
mask_idc
array([ 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 298, 299, 300,
301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77,
78, 79, 80, 81, 253, 254, 255, 256, 257, 258, 259, 260, 261,
262, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 226, 227, 89, 90,
91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41,
42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 235,
236, 237, 163, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, 287,
288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 224, 225, 226, 227,
228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 240, 241, 242, 243, 244, 245, 246,
247, 248, 249, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67,
59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 185, 186, 187,
188, 189, 190, 191, 192, 193, 194, 268, 269, 270, 271, 272, 273,
274, 275, 276, 277, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172,
173, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 298, 304, 305,
306, 307, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312, 313, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116,
117, 118, 119, 120, 121])
- 겹치는 frame & 총 frame 개수(315) 보다 큰거 제거
np.unique(mask_idc[mask_idc < sz])
array([ 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 58, 59, 60,
61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76,
77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89,
90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 102, 103, 104, 105,
106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 123, 124, 125, 126,
127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139,
140, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, 173, 174, 187, 188,
189, 190, 191, 192, 193, 194, 195, 196, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225,
226, 227, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 235, 236, 237, 238,
239, 240, 241, 242, 243, 257, 258, 259, 260, 261, 262, 263, 264,
265, 266, 268, 269, 270, 271, 272, 273, 274, 275, 276, 277, 288,
289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 303, 304, 305, 306,
307, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312])
- 각 example마다 위 과정을 거쳐 모든 batch 데이터에 대해서 mask indice산출
- 배치데이터를 생성하기 위해 짧은 길이의 mask length를 기준으로 concat
- 넘어가는 길이에 대해서는 최소길이 만큼 샘플로 같은 길이로 맞춤
- mask matrix는 초기에
False로 할당하고 mask할 위치에True를 부여
min_len = min([len(m) for m in mask_idcs])
for i, mask_idc in enumerate(mask_idcs):
if len(mask_idc) > min_len:
mask_idc = np.random.choice(mask_idc, min_len, replace=False)
mask[i, mask_idc] = True
mask
array([[False, False, False, ..., True, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
...,
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False],
[ True, True, True, ..., False, False, False],
[False, False, False, ..., False, False, False]])
mask.shape
(8, 315)
- projection된 feature의 현재 shape은
[8, 315, 768]이며,315에 특정 위치에 mask embedding vector([768])을 삽입해 줌
mask_indices = torch.from_numpy(mask_indices).to(x.device)
x[mask_indices] = self.mask_emb
- 결과적으로
self.apply_mask는 두개의 아웃풋을 생성
x, mask_indices = self.apply_mask(features, padding_mask)
x.shape # float
torch.Size([8, 315, 768])
mask_indices.shape # bool
torch.Size([8, 315])
y는 masking된 true embedding 값을 target으로 출력
y = unmasked_features[mask_indices].view(
unmasked_features.size(0), -1, unmasked_features.size(-1)
)
y.shape
torch.Size([8, 141, 512])
- Transformer encoder 구조에 feature를 넣게 됨
x = self.encoder(x, padding_mask=None)
# in self.encoder
'''
x.shape
torch.Size([8, 315, 768])
'''
x = self.extract_features(x, padding_mask)
- Encoder 연산과정은 다음과 같음
- Convolution: feature sequence와 동일하게 되도록 산출
Sequential( (0): Conv1d(768, 768, kernel_size=(128,), stride=(1,), padding=(64,), groups=16) (1): SamePad() (2): GELU() ) - skip-connection(
x += x_conv) - layer_norm(
x = self.layer_norm(x)) - dropout(
x = F.dropout(x, p=0.1)) - transformer 연산(layer droput: layer 자체를 dropout, 기준
self.layerdrop=0.05보다 너무 작으면 다음 레이어로 넘겨줌) - layernorm
- return
x: torch.Size([8, 315, 768])
- Convolution: feature sequence와 동일하게 되도록 산출
def extract_features(self, x, padding_mask=None):
if padding_mask is not None:
x[padding_mask] = 0
# x: torch.Size([8, 315, 768]) => torch.Size([8, 768, 315])
# x_conv: torch.Size([8, 768, 315])
x_conv = self.pos_conv(x.transpose(1, 2))
x_conv = x_conv.transpose(1, 2)
x += x_conv
if not self.layer_norm_first:
x = self.layer_norm(x)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
# B x T x C -> T x B x C
x = x.transpose(0, 1)
layer_results = []
for i, layer in enumerate(self.layers):
dropout_probability = np.random.random()
if not self.training or (dropout_probability > self.layerdrop):
x, z = layer(x, self_attn_padding_mask=padding_mask, need_weights=False)
layer_results.append(x)
# T x B x C -> B x T x C
x = x.transpose(0, 1)
return x
- quantizer 연산과정
mask target vector에 대한 quantization이 이루어짐
'''
self.quantizer
GumbelVectorQuantizer(
(weight_proj): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=640, bias=True)
)
y.shape
torch.Size([8, 141, 512]) # target vector in the masked indice
'''
q = self.quantizer(y, produce_targets=False)
def forward(self, x=y, produce_targets=False):
bsz, tsz, fsz = x.shape # torch.Size([8(bz), 141(seq), 512(in_dim)]) # orignal vec but be cloned
x = x.reshape(-1, fsz) # torch.Size([1128(seq*bz), 512(in_dim)])
x = self.weight_proj(x) # torch.Size([1128(seq*bz), 640(num_var *n_group)])
x = x.view(bsz * tsz * self.groups, -1) # torch.Size([2256(seq*bz*n_group), 320(num_var )])
_, k = x.max(-1) # 각 group axis에서 큰 값의 위치를 추출
hard_x은 onehot vector를 만들듯이 320차원의 logit 값이 가장 큰 부분에 1을 할당
hard_x = (
x.new_zeros(*x.shape) # torch.Size([2256, 320])
.scatter_(-1, k.view(-1, 1), 1.0) # 마지막 축에 대하여 k indice에 해당하는 부분에 1.0을 할당
.view(bsz * tsz, self.groups, -1) # reshape
)
hard_x.shape
torch.Size([1128, 2, 320]) # (seq*bz, n_group, num_var )
Loss
- 각 observation
seq*bz에 대해서 loss 산출 - loss는 각 group에 대해서 취합(
sum)됨
code_perplexity: 각 group에 대해서 320차원을 가진 확률 분포를 정의 후, entropy 계산 \(p=\text{hard}_{prop}\) \(entropy = \exp ( -\sum p \log p )\)
hard_probs = torch.mean(hard_x.float(), dim=0)
hard_probs.shape
torch.Size([2, 320])
result["code_perplexity"] = torch.exp(
-torch.sum(hard_probs * torch.log(hard_probs + 1e-7), dim=-1)
).sum()
prob_perplexity- feature map $\mathbf{h}$를 feature dim에 대해서 softmax를 취한 후
batch_size*sequence에 대해서 평균 - 다양한 Quantization이 되도록 perplexity를 최대화하는 것이 목적
- Batch statics: 각 샘플, 타임 별로 개별 codebook의 평균 softmax를 구함
- feature map $\mathbf{h}$를 feature dim에 대해서 softmax를 취한 후
\(p = \text{softmax } \textbf{h}\) \(\)
avg_probs = torch.softmax(
x.view(bsz * tsz, self.groups, -1).float(), dim=-1
).mean(dim=0) # torch.Size([2, 320])
result["prob_perplexity"] = torch.exp(
-torch.sum(avg_probs * torch.log(avg_probs + 1e-7), dim=-1)
).sum()
F.gumbel_softmax는 feature 의 temperature scaling한 후 가장 높은 logit에 대하여 onehot vecotor 처리hard_x와 동일한 과정이지만, temperature scaling를 사용하고, argmax가 미분 불가능점을 고려해F.gumbel_softmax를 사용한 것 같음if self.training: x = F.gumbel_softmax(x.float(), tau=self.curr_temp, hard=True).type_as(x) else: x = hard_x- softmax prob에 대해서 320(num_var)에 대해서 summation
x = x.view(bsz * tsz, -1) # torch.Size([1128(bz*seq), 640(n_group*num_var )])
vars = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, num_groups * num_vars, var_dim))
'''
x.unsqueeze(-1).shape
torch.Size([1128, 640, 1])
vars.shape # initialized
torch.Size([1, 640, 128])
'''
x = x.unsqueeze(-1) * vars # torch.Size([1128, 640, 128])
x = x.view(bsz * tsz, self.groups, self.num_vars, -1) # torch.Size([1128(bz*seq), 2(n_group), 320(num_var), 128(var_dim)])
x = x.sum(-2) # torch.Size([1128(bz*seq), 2(n_group), 128(var_dim)])
x = x.view(bsz, tsz, -1) # torch.Size([8(bz), 141(seq), 256(n_group*var_dim)])
- 위 과정에서 산출된 값이
q["x"]
q = self.quantizer(y, produce_targets=False)
q["x"].shape
torch.Size([8, 141, 256])
- 추가로 linear projection 수행
y= q["x"]
y = self.project_q(y)
y.shape
torch.Size([8, 141, 256])
sample_negatives: masked sequence(141)범위에서 각 negative sample(100)를 추출neg: 추출된 negative sample 임베딩- 왼쪽에 더 (음성이시작되는 부분에) negative sample이 되도록 수정
- e.g.
[True, False, False, False, True, False]->[True, False, True, False, False, False]
negs, _ = self.sample_negatives(y, y.size(1))
num = y.size(1) # 141
bsz, tsz, fsz = y.shape
y = y.view(-1, fsz) # BTC => (BxT)C # torch.Size([1128, 256])
if self.n_negatives > 0:
tszs = (
buffered_arange(num) # torch.Size([141])
.unsqueeze(-1) # torch.Size([141, 1])
.expand(-1, self.n_negatives) # torch.Size([141, 100]), hstack
.flatten() # torch.Size([14100])
)
neg_idxs = torch.randint(
low=0, high=high - 1, size=(bsz, self.n_negatives * num)
) # torch.Size([8, 14100])
'''
tensor([[105, 59, 4, ..., 69, 34, 117],
[ 78, 132, 35, ..., 17, 125, 58],
[ 92, 101, 74, ..., 100, 64, 106],
...,
[ 45, 10, 128, ..., 68, 95, 36],
[ 31, 82, 96, ..., 46, 42, 69],
[115, 67, 131, ..., 3, 108, 33]])
'''
neg_idxs[neg_idxs >= tszs] += 1 # torch.Size([8, 14100]) # 왼쪽에 더 (음성이시작되는 부분에) negative sample이 되도록 수정
'''
tensor([[106, 60, 5, ..., 69, 34, 117],
[ 79, 133, 36, ..., 17, 125, 58],
[ 93, 102, 75, ..., 100, 64, 106],
...,
[ 46, 11, 129, ..., 68, 95, 36],
[ 32, 83, 97, ..., 46, 42, 69],
[116, 68, 132, ..., 3, 108, 33]])
'''
negs = y[neg_idxs.view(-1)] # torch.Size([112800, 256]) # negative samples seleted
negs = negs.view( # torch.Size([8, 141, 100, 256])
bsz, num, self.n_negatives + self.cross_sample_negatives, fsz
).permute(
2, 0, 1, 3
) # to torch.Size([100, 8, 141, 256])
- neg_idxs
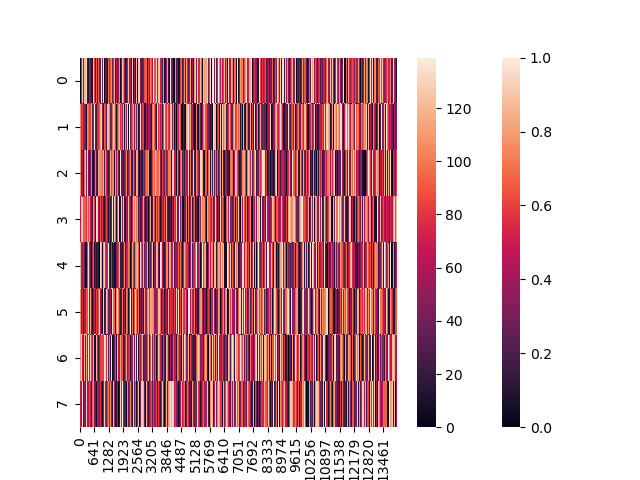
- neg_idxs[neg_idxs >= tszs] += 1
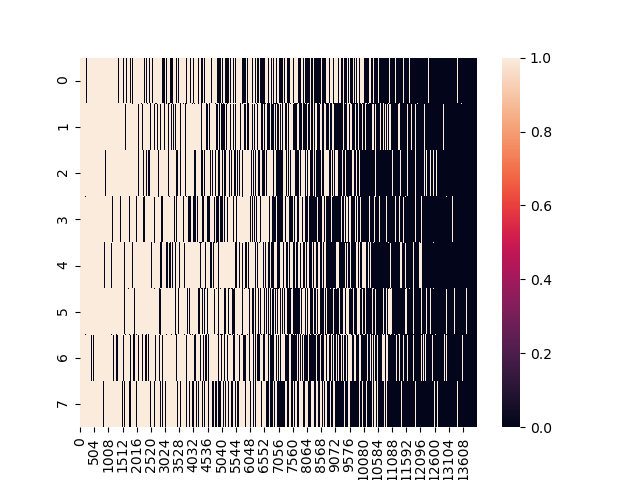
- mask_indice
mask_indices.shape
(8, 315) #(bz, audio_seq)
# embedding vector에서 mask된 부분을 추출
x = x[mask_indices].view(x.size(0), -1, x.size(-1))
x.shape # torch.Size([8, 141, 768])
- linear projection
self.final_proj
Linear(in_features=768, out_features=256, bias=True)
x = self.final_proj(x)
x.shape # torch.Size([8, 141, 256])
neg_is_pos: neg_sample, batch, mask_seq에 매칭이 되는 부분 선택targets: 1개의 true label이 존재하고, 100개의 negative label이 존재, 분류 task- 실제 타켓과 겹치는 negative sample 부분은
-inf로 처리
'''
x.shape: torch.Size([8, 141, 256]) # masked original vectors
y.shape: torch.Size([8, 141, 256]) # target vectors in the mask locations
negs.shape : torch.Size([100, 8, 141, 256]) # 100개 neg 샘플링 in 141 masked range
'''
x = self.compute_preds(x, y, negs)
def compute_preds(self, x, y, negatives):
neg_is_pos = (y == negatives).all(-1) # (y == negatives).shape : torch.Size([100, 8, 141, 256])
y = y.unsqueeze(0) # torch.Size([1, 8, 141, 256])
targets = torch.cat([y, negatives], dim=0) # torch.Size([101, 8, 141, 256])
logits = torch.cosine_similarity(x.float(), targets.float(), dim=-1).type_as(x) # torch.Size([101, 8, 141])
logits /= self.logit_temp
if neg_is_pos.any():
logits[1:][neg_is_pos] = float("-inf")
return logits # torch.Size([101, 8, 141])
loss stage
logits = model.get_logits(net_output).float()
def get_logits(self, net_output):
logits = net_output["x"] # torch.Size([101, 8, 141])
logits = logits.transpose(0, 2) # torch.Size([141, 8, 101])
logits = logits.reshape(-1, logits.size(-1)) # torch.Size([1128, 101])
return logits
target = model.get_targets(sample, net_output)
def get_targets(self, sample, net_output, expand_steps=True):
x = net_output["x"] # torch.Size([101, 8, 141])
return x.new_zeros(x.size(1) * x.size(2), dtype=torch.long) # torch.Size([1128]), 0th true label is located
- 0번째에 true label이 존재, 해당 0번째 logit으로 커지도록 cross entropy 사용
if self.infonce:
loss = F.cross_entropy(
logits,
target,
reduction="sum" if reduce else "none",
)
- 2개의 추가 loss 생성
prob_perplexity: masked true vector prob(softmax) entropyfeatures_pen: feature 벡터의 제곱합으로 regularization
def get_extra_losses(self, net_output):
pen = []
if "prob_perplexity" in net_output:
pen.append(
(net_output["num_vars"] - net_output["prob_perplexity"])
/ net_output["num_vars"]
)
if "features_pen" in net_output:
pen.append(net_output["features_pen"]) # x^2
return pen
- 생성된 두개의 loss를 사전에 정의해논
loss_weight = [0.1, 10.0]를 반영하여 loss 가중치를 주고, 샘플수로 정규화해 줌
for p, coef in zip(extra_losses, self.loss_weights):
if coef != 0 and p is not None:
p = coef * p.float() * sample_size
loss += p
losses.append(p)
- 최종 3개의 loss가 반영됨
- minimize cross_entropy
- maximize prob_perplexity
- minimize feature_pen (conv layer 후, 임베딩 된 벡터의 제곱 합)
# features: torch.Size([8, 315, 512])
features_pen = features.float().pow(2).mean()
logging_output = {
"loss": loss.item() if reduce else loss, # cross_entropy, prob_perplexity, feature_pen
"ntokens": sample_size,
"nsentences": sample["id"].numel(),
"sample_size": sample_size,
}
